Júlio Gabriel Chilela

Background:
- Trainee at the University of Houston, Texas, United States of America
- M.Sc. Geographic Information Technology, University of Coimbra, Portugal
- B.Sc. Computer Science for Education, ISCED – Huíla, Angola
Contact:
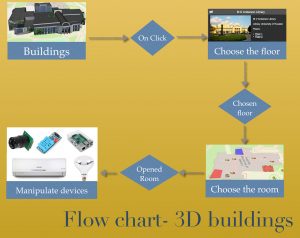
Think about a 3D map that the user has the possibility of clicking on the building, choosing the floor, opening the room and picking the device to perform a specific task.
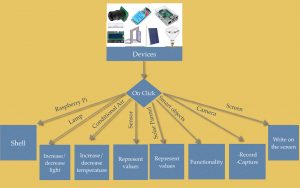
Smart devices deployed around the city and facilities can be manipulated directly through the map. When the user clicks on the device, the map shows a menu for performing tasks.
Nowadays, data visualization is extremely important in many fields of the modern world.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is growing very fast. Sensors are widespread, as well as cameras, smart lamps, smart doors, traffic lights, solar panels, air conditioning and the immeasurable number of smart objects. It is extremely important to improve models, develop patterns and enhance the analysis of huge amounts of data. It is also important to build systems to extract information efficiently in order to make accurate decisions.
The scope of my research in the Wireless and Optical Network Lab is to integrate the usage of Web Geographic Information Systems (WebGIS) in smart cities and facilities management for data visualization, analysis, and to provide interaction between citizens and between citizens and smart city.
Geographic Information Systems in the web are integrated to provide maps in 3D of the city buildings and all smart city information in layers.
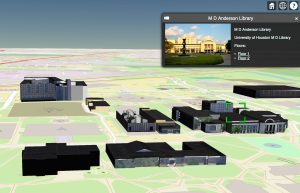
The goal is to develop a WebGIS capable of saving, organizing and geo-spatializing the IoT’s information from all over the city and facilities. In addition, it will provide mobile applications to allow citizens to interact with smart cities, as well as city facilities, while also providing easy access to information like data from sensors, cameras, and smart objects which have been placed in various locations around the city. This information could include information about city’s administration, number of people inside public buildings, and so on.
Users of mobile application can inform maintenance staff of infrastructure failure via photographic data. Citizens can also interact through the mobile application regarding various cities conditions such as road hazards, as well as request facility temperature and lighting changes in some specific buildings.
This type of system allows smart cities administrators to interact with the devices installed in facilities around city through the map as well as have access to different information of devices in dashboards.
In order to achieve the objectives, I am using different programing languages to create scripts for controlling and interacting with devices, but overall, I am using the Python-Django framework and GeoDjango.